Robotic-assisted right upper lobectomy
Clinical data
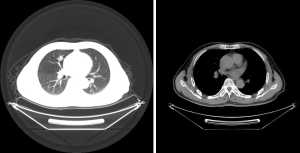
The patient was a 71-year-old man admitted because of cough and expectoration lasting a week. Chest computed tomography (CT) (Figure 1) showed a nodular shadow on the right upper lobe of the lung. The local hospital considered the possibility of inflammation, and cough improved after anti-inflammatory treatment. A second CT scan showed that the lesions did not shrink. The patient even visited our hospital again. Positron emission tomography (PET)-CT findings were highly suggestive of lung cancer. The patient̓ s cardiopulmonary function, blood gas analysis, and laboratory tests were normal. There was no positive sign or supraclavicular lymph node enlargement on physical examination. He had a history of diabetes (5 years). Twenty years previously, he underwent surgery for the gallbladder stones.
Operation steps
Anesthesia and body position
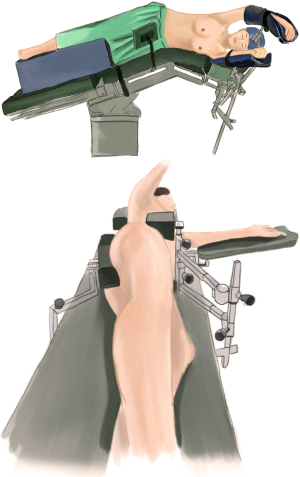
The patient received general anesthesia by double-lumen endotracheal intubation and was placed in the lateral decubitus position and in a jackknife position with single-lung (left) ventilation (1) (Figure 2).
Ports
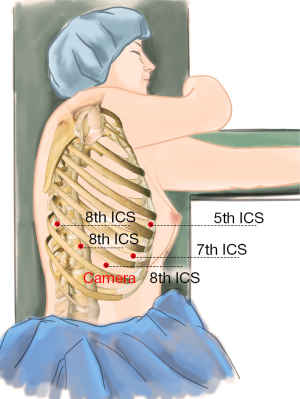
A 1.5-cm camera port (for a 12-mm trocar) was placed in the 8th intercostal space (ICS) at the right middle axillary line, and three separate 1.0-cm working ports (for 8-mm trocars) were made in the 5th ICS (#1 arm) at the right anterior axillary line, the 8th ICS (#2 arm) at the right posterior axillary line, and the right 8th ICS (#3 arm), 2 cm from the spine. An auxiliary port (for a 12-mm trocar) was made in the 7th ICS near the costal arch (2) (Figure 3).
Installation of the surgical arms
The robot patient cart was positioned directly above the operating table and then connected. The #2 arm was connected to a bipolar cautery forceps, and the #1 arm was connected to a unipolar cautery hook. An incision protector was used in the auxiliary port (3).
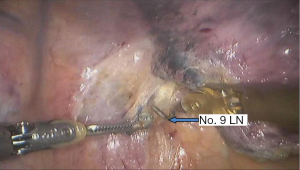
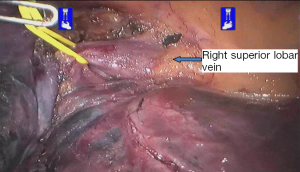
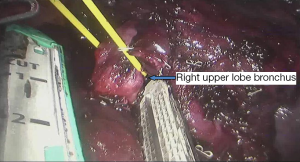
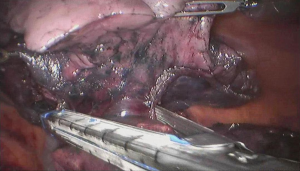
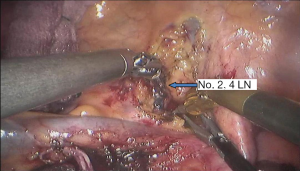
Surgical procedure (see Figures 4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14)
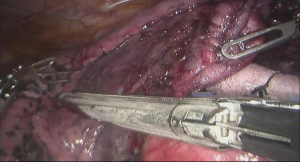
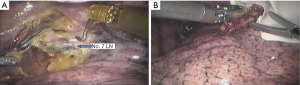
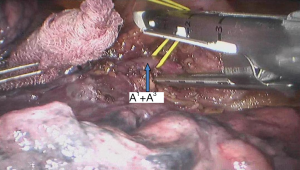
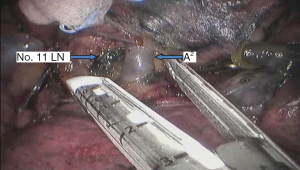
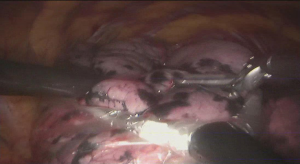
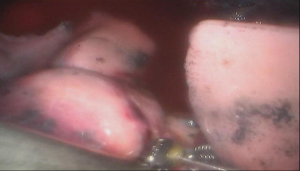
Postoperative condition
Postoperative treatments included anti-inflammation and phlegm-resolving treatment. The thoracic drainage tube was withdrawn 2 days after surgery, and the patient was discharged 3 days after surgery. No complications were observed during hospitalization. Pathological diagnosis was invasive adenocarcinoma (2.0 cm × 1.5 cm × 1.0 cm) in the right upper pulmonary lobe. No metastasis was seen at the bronchial stump or the sampled lymph nodes. The pathological stage: pT1aN0M0, IA stage.
Acknowledgements
Funding: None.
Footnote
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/amj.2017.01.08). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical Statement: The authors are accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee(s) and with the Helsinki Declaration (as revised in 2013). Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this manuscript and any accompanying images.
Open Access Statement: This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), which permits the non-commercial replication and distribution of the article with the strict proviso that no changes or edits are made and the original work is properly cited (including links to both the formal publication through the relevant DOI and the license). See: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
References
- Xu S, Wang T, Xu W, et al. Robotic-assisted right upper lobectomy. Ann Transl Med 2015;3:170. [PubMed]
- Park BJ, Flores RM, Rusch VW. Robotic assistance for video-assisted thoracic surgical lobectomy: technique and initial results. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2006;131:54-9. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Cerfolio RJ, Bryant AS. Robotic-assisted pulmonary resection - Right upper lobectomy. Ann Cardiothorac Surg 2012;1:77-85. [PubMed]
Cite this article as: Du H, Yang S, Guo W, Jin R, Zhang Y, Chen X, Wu H, Han D, Chen K, Xiang J, Li H. Robotic-assisted right upper lobectomy. AME Med J 2017;2:6.