Penile condyloma acuminata managed by resection and full thickness skin graft
Condyloma acuminata or Buschke-Lowenstein tumor is a budding lesion due to infection by human papilloma virus (HPV) of genotypes 6 and 11. The transmission is essentially sexual.
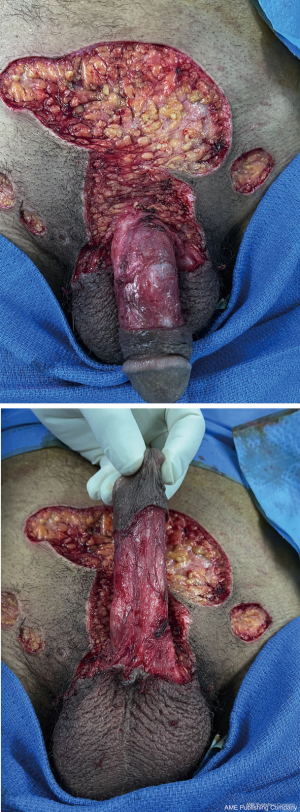
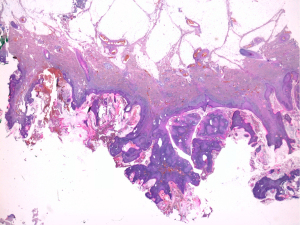
We report the case of a 54-year-old patient, with no medical history, complaining of a lesion in the hypogastric and penile region (Figure 1). History revealed that the lesion onset goes back to 7 years with an ulcero-budding lesion of the hypogastric region. The progression has known the appearance of other lesions with extension to the penis. The rest of the skin examination shows no anal localization, no urethral discharge. A biopsy of the lesion was made, providing the diagnosis of condyloma acuminata (Figures 2,3).
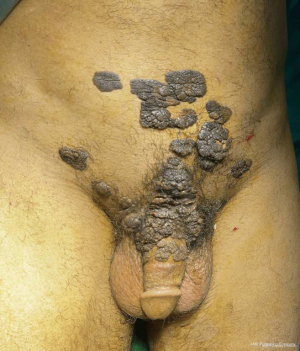

The reference treatment for extended warts is total resection, non-surgical treatment is reserved for non-extended forms.
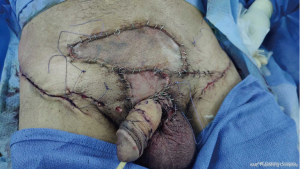
Our case benefited from multidisciplinary care including urology and plastic surgery, the patient underwent an extensive resection of the condyloma taking the hypogastric and penile region (Figure 4) with reconstruction by skin graft taken from the bilateral inguinal region (Figure 5).
Full-thickness skin grafts (FTSG) and split-thickness skin grafts (STSG) are two options that have been reported for penile skin reconstruction. However, split-thickness skin grafts has a higher risk of shrinkage which can affect erection.
Acknowledgments
Funding: None.
Footnote
Peer Review File: Available at https://amj.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/amj-23-20/prf
Conflicts of Interest: Both authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://amj.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/amj-23-20/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical Statement: The authors are accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee(s) and with the Helsinki Declaration (as revised in 2013). Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of these “Images in Clinical Medicine”. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the editorial office of this journal.
Open Access Statement: This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), which permits the non-commercial replication and distribution of the article with the strict proviso that no changes or edits are made and the original work is properly cited (including links to both the formal publication through the relevant DOI and the license). See: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
Cite this article as: Irzi M, Barki A. Penile condyloma acuminata managed by resection and full thickness skin graft. AME Med J 2023;8:20.